
|
|
The
Proper use of labels with the elements above will benefit:
Tips and NotesTip: The for attribute of Browser Support
|
Create a HTML <label> Tag
Three radio buttons with labels.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<input type="radio" id="html" name="fav_language" value="HTML">
<label for="html">HTML</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="css" name="fav_language" value="CSS">
<label for="css">CSS</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="javascript" name="fav_language" value="JavaScript">
<label for="javascript">JavaScript</label><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <label> for Attribute
Three radio buttons with labels:
Definition and Usage
The for attribute specifies which form element a label is bound to.
Browser Support

Syntax
<label for="element_id">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| element_id | The id of the element the label is bound to |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<input type="radio" id="html" name="fav_language" value="HTML">
<label for="html">HTML</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="css" name="fav_language" value="CSS">
<label for="css">CSS</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="javascript" name="fav_language" value="JavaScript">
<label for="javascript">JavaScript</label><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <label> form Attribute
A <label> element located outside a form (but still a part of the form):
Definition and Usage
The form attribute specifies the form the label belongs to.
The value of this attribute must be equal to the id attribute of a <form> element in the same document.
Browser Support

Syntax
<label form="form_id">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| form_id | Specifies the form element the <label> element belongs to. The value of this attribute must be the id attribute of a <form> element in the same document. |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php" id="form1">
<input type="radio" id="html" name="fav_language" value="HTML"><br>
<input type="radio" id="css" name="fav_language" value="CSS">
<label for="css">CSS</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="javascript" name="fav_language" value="JavaScript">
<label for="javascript">JavaScript</label><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<label form="form1" for="html">HTML</label>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="checkbox"> label Tag
Let the user select one or more options of a limited number of choices:
Definition and Usage
The <input type="checkbox"> defines a checkbox.
The checkbox is shown as a square box that is ticked (checked) when activated.
Checkboxes are used to let a user select one or more options of a limited number of choices.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support

Syntax
<input type="checkbox">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<input type="checkbox" id="vehicle1" name="vehicle1" value="Bike">
<label for="vehicle1"> I have a bike</label><br>
<input type="checkbox" id="vehicle2" name="vehicle2" value="Car">
<label for="vehicle2"> I have a car</label><br>
<input type="checkbox" id="vehicle3" name="vehicle3" value="Boat">
<label for="vehicle3"> I have a boat</label><br>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="color"> label Tag
Show a color picker (with a predefined red value):
Definition and Usage
The <input type="color"> defines a color picker.
The default value is #000000 (black). The value must be in seven-character hexadecimal notation.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="color">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="favcolor">Select your favorite color:</label>
<input type="color" id="favcolor" name="favcolor" value="#ff0000">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="date"> label Tag
Show a date control:
Definition and Usage
The <input type="date"> defines a date picker.
The resulting value includes the year, month, and day.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="date">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="birthday">Birthday:</label>
<input type="date" id="birthday" name="birthday">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="datetime-local"> label Tag
Show a date and time control (no timezone) :
Definition and Usage
The <input type="datetime-local"> defines a date picker.
The resulting value includes the year, month, day, and time.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="datetime-local">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="birthdaytime">Birthday (date and time):</label>
<input type="datetime-local" id="birthdaytime" name="birthdaytime">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="email"> label Tag
Define a field for an e-mail address (validates automatically when submitted):
Definition and Usage
The <input type="email"> defines a field for an e-mail address.
The input value is automatically validated to ensure it is a properly formatted e-mail address.
To define an e-mail field that allows multiple e-mail addresses, add the "multiple" attribute.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="email">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="email">Enter your email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="file"> label Tag
Define a file-select field:
Definition and Usage
The <input type="file"> defines a file-select field and a "Browse" button for file uploads.
To define a file-select field that allows multiple files to be selected, add the multiple attribute.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="file">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="myfile">Select a file:</label>
<input type="file" id="myfile" name="myfile">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="month"> label Tag
Define a month and year control (no time zone):
Definition and Usage
The <input type="month"> defines a month and year control.
The format is "YYYY-MM".
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="month">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="bdaymonth">Birthday (month and year):</label>
<input type="month" id="bdaymonth" name="bdaymonth">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="number"> label Tag
Define a field for entering a number (You can also set restrictions on what numbers are accepted):
Definition and Usage
The <input type="number"> defines a field for entering a number.
Use the following attributes to specify restrictions:
- max - specifies the maximum value allowed
- min - specifies the minimum value allowed
- step - specifies the legal number intervals
- value - Specifies the default value
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support

Syntax
<input type="number">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="quantity">Quantity (between 1 and 5):</label>
<input type="number" id="quantity" name="quantity" min="1" max="5">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input> max Attribute label Tag
Use of the min and max attributes.
Definition and Usage
The max attribute specifies the maximum value for an <input> element.
Tip: Use the max attribute together with the min attribute to create a range of legal values.
Note: The max and min attributes works with the following input types: number, range, date, datetime-local, month, time and week.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<input max="number|date">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies the maximum value allowed |
| date | Specifies the maximum date allowed |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="datemax">Enter a date before 1980-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemax" name="datemax" max="1979-12-31"><br><br>
<label for="datemin">Enter a date after 2000-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemin" name="datemin" min="2000-01-02"><br><br>
<label for="quantity">Quantity (between 1 and 5):</label>
<input type="number" id="quantity" name="quantity" min="1" max="5"><br><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input> max Number Attribute label Tag
| number | Specifies the maximum value allowed |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="quantity">Quantity (between 1 and 5):</label>
<input type="number" id="quantity" name="quantity" min="1" max="5">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input> max Date Attribute label Tag
Use of the min and max attributes.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="datemax">Enter a date before 1980-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemax" name="datemax" max="1979-12-31"><br><br>
<label for="datemin">Enter a date after 2000-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemin" name="datemin" min="2000-01-02"><br><br>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input> min Attribute on label Tag
Use of the min and max attributes.
Definition and Usage
The min attribute specifies the minimum value for an <input> element.
Tip: Use the min attribute together with the max attribute to create a range of legal values.
Note: The max and min attributes works with the following input types: number, range, date, datetime-local, month, time and week.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<input min="number|date">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies the minimum value allowed |
| date | Specifies the minimum date allowed |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="quantity">Quantity (between 1 and 5):</label>
<input type="number" id="quantity" name="quantity" min="1" max="5">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input> min number Attribute on label Tag
| number | Specifies the minimum value allowed |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="quantity">Quantity (between 1 and 5):</label>
<input type="number" id="quantity" name="quantity" min="1" max="5">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input> min date Attribute on label Tag
| date | Specifies the minimum date allowed |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="datemax">Enter a date before 1980-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemax" name="datemax" max="1979-12-31"><br><br>
<label for="datemin">Enter a date after 2000-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemin" name="datemin" min="2000-01-02"><br><br>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input> step Attribute label Tag
An HTML form with an input field with a specified legal number intervals.
Definition and Usage
The step attribute specifies the interval between legal numbers in an <input> element.
Example: if step="3", legal numbers could be -3, 0, 3, 6, etc.
Tip: The step attribute can be used together with the max and min attributes to create a range of legal values.
Note: The step attribute works with the following input types: number, range, date, datetime-local, month, time and week.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.
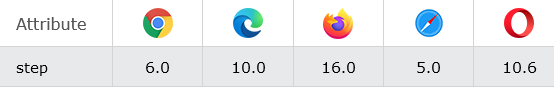
Syntax
<input step="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies the interval between legal numbers in the input field. Default is 1 |
| any |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="points">Points:</label>
<input type="number" id="points" name="points" step="3">
<input type="submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input> value Attribute label Tag
An HTML form with initial (default) values.
Definition and Usage
The value attribute specifies the value of an <input> element.
The value attribute is used differently for different input types:
- For "button", "reset", and "submit" - it defines the text on the button
- For "text", "password", and "hidden" - it defines the initial (default) value of the input field
- For "checkbox", "radio", "image" - it defines the value associated with the input (this is also the value that is sent on submit)
Note: The value attribute cannot be used with <input type="file">.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<input value="text">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| text | Specifies the value of the <input> element |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="password"> on label Tag
Define a password field (characters are masked).
Definition and Usage
The <input type="password"> defines a password field (characters are masked).
Note: Any forms involving sensitive information like passwords should be served over HTTPS.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support

Syntax
<input type="password">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email"><br><br>
<label for="pwd">Password:</label>
<input type="password" id="pwd" name="pwd" minlength="8"><br><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="radio"> on label Tag
Radio buttons let a user select only one of a limited number of choices.
Definition and Usage
The <input type="radio"> defines a radio button.
Radio buttons are normally presented in radio groups (a collection of radio buttons describing a set of related options). Only one radio button in a group can be selected at the same time.
Note: The radio group must share the same name (the value of the name attribute) to be treated as a group. Once the radio group is created, selecting any radio button in that group automatically deselects any other selected radio button in the same group. You can have as many radio groups on a page as you want, as long as each group has its own name.
Note: The value attribute defines the unique value associated with each radio button. The value is not shown to the user, but is the value that is sent to the server on "submit" to identify which radio button that was selected.
Browser Support

Syntax
<input type="radio">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<p>Please select your favorite Web language:</p>
<input type="radio" id="html" name="fav_language" value="HTML">
<label for="html">HTML</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="css" name="fav_language" value="CSS">
<label for="css">CSS</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="javascript" name="fav_language" value="JavaScript">
<label for="javascript">JavaScript</label>
<br>
<p>Please select your age:</p>
<input type="radio" id="age1" name="age" value="30">
<label for="age1">0 - 30</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="age2" name="age" value="60">
<label for="age2">31 - 60</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="age3" name="age" value="100">
<label for="age3">61 - 100</label><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="range"> on label Tag
Define a range control (like a slider control).
Definition and Usage
The <input type="range"> defines a control for entering a number whose exact value is not important (like a slider control).
Default range is 0 to 100. However, you can set restrictions on what numbers are accepted with the attributes below.
- max - specifies the maximum value allowed
- min - specifies the minimum value allowed
- step - specifies the legal number intervals
- value - Specifies the default value
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="range">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="vol">Volume (between 0 and 50):</label>
<input type="range" id="vol" name="vol" min="0" max="50">
<input type="submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="range"> Max Attribute on label Tag
Use of the min and max attributes.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="vol">Volume (between 0 and 50):</label>
<input type="range" id="vol" name="vol" min="0" max="50">
<input type="submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="range"> Min Attribute on label Tag
Use of the min and max attributes.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="vol">Volume (between 0 and 50):</label>
<input type="range" id="vol" name="vol" min="0" max="50">
<input type="submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="search"> on label Tag
Define a search field (like a site search, or Google search).
Definition and Usage
The <input type="search"> defines a text field for entering a search string.
Note: Remember to set a name for the search field, otherwise nothing will be submitted. The most common name for search inputs is q.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="search">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="gsearch">Search Google:</label>
<input type="search" id="gsearch" name="gsearch">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="tel"> on label Tag
Define a field for entering a telephone number.
Definition and Usage
The <input type="tel"> defines a field for entering a telephone number.
Note: Browsers that do not support "tel" fall back to being a standard "text" input.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support

Syntax
<input type="tel">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="phone">Enter your phone number:</label>
<input type="tel" id="phone" name="phone" pattern="[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{3}">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="text"> on label Tag
Define a single-line text field that a user can enter text into.
Definition and Usage
The <input type="text"> defines a single-line text field.
The default width of the text field is 20 characters.
Browser Support

Syntax
<input type="text">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="time"> on label Tag
Definition and Usage
The <input type="time"> defines a control for entering a time (no time zone).
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="time">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="appt">Select a time:</label>
<input type="time" id="appt" name="appt">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="url"> on label Tag
Define a field for entering a URL.
Definition and Usage
The <input type="url"> defines a field for entering a URL.
The input value is automatically validated before the form can be submitted.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="url">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="homepage">Add your homepage:</label>
<input type="url" id="homepage" name="homepage">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <input type="week"> on label Tag
Define a week and year control (no time zone).
Definition and Usage
The <input type="week"> defines a week and year control (no time zone).
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Syntax
<input type="week">
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="week">Select a week:</label>
<input type="week" id="week" name="week">
Output should be:

How to add HTML <meter> with label Tag
Use the meter element to display a scalar value within a given range (a gauge).
Definition and Usage
The <meter> tag defines a scalar measurement within a known range, or a fractional value. This is also known as a gauge.
Examples: Disk usage, the relevance of a query result, etc.
Note: The <meter> tag should not be used to indicate progress (as in a progress bar). For progress bars, use the <progress> tag.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| form | form_id | Specifies which form the <meter> element belongs to |
| high | number | Specifies the range that is considered to be a high value |
| low | number | Specifies the range that is considered to be a low value |
| max | number | Specifies the maximum value of the range |
| min | number | Specifies the minimum value of the range. Default value is 0 |
| optimum | number | Specifies what value is the optimal value for the gauge |
| value | number | Required. Specifies the current value of the gauge |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="disk_c">Disk usage C:</label>
<meter id="disk_c" value="2" min="0" max="10">2 out of 10</meter><br>
<label for="disk_d">Disk usage D:</label>
<meter id="disk_d" value="0.6">60%</meter>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <meter> form Attribute with label Tag
A <meter> element located outside a form (but still a part of the form).
Definition and Usage
The form attribute specifies the form the <meter> tag belongs to.
The value of this attribute must be equal to the id attribute of a <meter> element in the same document.
Browser Support

Syntax
<meter form="form_id">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| form_id | Specifies the form element the <meter> element belongs to. The value of this attribute must be the id attribute of a <form> element in the same document. |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php" method="get" id="form1">
First name: <input type="text" name="fname"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<p><label for="anna">Anna's score:</label>
<meter id="anna" form="form1" name="anna" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="95"></meter></p>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <meter> high Attribute with label Tag
A gauge with a current value and min, max, high, and low segments.
Definition and Usage
The high attribute specifies the range where the gauge's value is considered to be a high value.
The high attribute value must be less than the max attribute value, and it also must be greater than the low and min attribute values.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<meter high="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies a floating point number that is considered to be a high value |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<p><label for="anna">Anna's score:</label>
<meter id="anna" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="95"></meter></p>
<p><label for="peter">Peter's score:</label>
<meter id="peter" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="65"></meter></p>
<p><label for="linda">Linda's score:</label>
<meter id="linda" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="35"></meter></p>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <meter> low Attribute with label Tag
A gauge with a current value and min, max, high, and low segments.
Definition and Usage
The low attribute specifies the range where the gauge's value is considered to be a low value.
The low attribute value must be greater than the min attribute value, and it also must be less than the high and max attribute values.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<meter low="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies a floating point number that is considered to be a low value |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<p><label for="anna">Anna's score:</label>
<meter id="anna" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="95"></meter></p>
<p><label for="peter">Peter's score:</label>
<meter id="peter" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="65"></meter></p>
<p><label for="linda">Linda's score:</label>
<meter id="linda" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="35"></meter></p>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <meter> max Attribute with label Tag
A gauge with a current value and min, max, high, and low segments.
Definition and Usage
The max attribute specifies the upper bound of the gauge.
The max attribute value must be greater than the min attribute value.
If unspecified, the default value is 1.
Tip: The max attribute, together with the min attribute, specifies the full range of the gauge.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<meter max="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies a floating point number that is the maximum value of the gauge. Default value is "1" |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<p><label for="anna">Anna's score:</label>
<meter id="anna" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="95"></meter></p>
<p><label for="peter">Peter's score:</label>
<meter id="peter" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="65"></meter></p>
<p><label for="linda">Linda's score:</label>
<meter id="linda" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="35"></meter></p>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <meter> min Attribute with label Tag
A gauge with a current value and min, max, high, and low segments.
Definition and Usage
The min attribute specifies the lower bound of the gauge.
The min attribute value must be less than the max attribute value.
If unspecified, the default value is 0.
Tip: The min attribute, together with the max attribute, specifies the full range of the gauge.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<meter min="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies a floating point number that is the minimum value of the gauge. Default value is 0 |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<p><label for="anna">Anna's score:</label>
<meter id="anna" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="95"></meter></p>
<p><label for="peter">Peter's score:</label>
<meter id="peter" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="65"></meter></p>
<p><label for="linda">Linda's score:</label>
<meter id="linda" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="35"></meter></p>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <meter> optimum Attribute with label Tag
A gauge with an optimal value of 0.5.
Definition and Usage
The optimum attribute specifies the range where the gauge's value is considered to be an optimal value.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<meter optimum="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies a floating point number that is the optimal value of the gauge |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<p><label for="yinyang">Yin Yang:</label>
<meter id="yinyang" value="0.3" high="0.9" low="0.1" optimum="0.5"></meter></p>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <meter> value Attribute with label Tag
A gauge with a current value and min, max, high, and low segments.
Definition and Usage
The required value attribute specifies the current, or "measured", value of the gauge.
The value attribute must be between the min and max attribute values.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<meter value="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Required. Specifies a floating point number that is the current value of the gauge |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<p><label for="anna">Anna's score:</label>
<meter id="anna" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="95"></meter></p>
<p><label for="peter">Peter's score:</label>
<meter id="peter" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="65"></meter></p>
<p><label for="linda">Linda's score:</label>
<meter id="linda" min="0" low="40" high="90" max="100" value="35"></meter></p>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <progress> Tag with label Tag
Show a progress bar.
Definition and Usage
The <progress> tag represents the completion progress of a task.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Tips and Notes
Tip: Use the <progress> tag in conjunction with JavaScript to display the progress of a task.
Note: The <progress> tag is not suitable for representing a gauge (e.g. disk space usage or relevance of a query result). To represent a gauge, use the <meter> tag instead.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.

Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| max | number | Specifies how much work the task requires in total. Default value is 1 |
| value | number | Specifies how much of the task has been completed |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="file">Downloading progress:</label>
<progress id="file" value="32" max="100"> 32% </progress>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <progress> max Attribute with label Tag
Show a progress bar.
Definition and Usage
The max attribute specifies how much work the task requires in total.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<progress max="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | A floating point number that specifies how much work the task requires in total before it can be considered complete. Default value is 1. |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="file">Downloading progress:</label>
<progress id="file" value="32" max="100"> 32% </progress>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <progress> value Attribute with label Tag
Definition and Usage
The value attribute specifies how much of the task has been completed.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<progress value="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | A floating point number that specifies how much of the task has been completed |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="file">Downloading progress:</label>
<progress id="file" value="32" max="100"> 32% </progress>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <select> Attribute with label Tag
Create a drop-down list with four options.
Definition and Usage
The <select> element is used to create a drop-down list.
The <select> element is most often used in a form, to collect user input.
The name attribute is needed to reference the form data after the form is submitted (if you omit the name attribute, no data from the drop-down list will be submitted).
The id attribute is needed to associate the drop-down list with a label.
The <option> tags inside the <select> element define the available options in the drop-down list.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support

index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="cars">Choose a car:</label>
<select name="cars" id="cars">
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
<option value="mercedes">Mercedes</option>
<option value="audi">Audi</option>
</select>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <select> autofocus Attribute with label Tag
A drop-down list with autofocus.
Definition and Usage
The autofocus attribute is a boolean attribute.
When present, it specifies that the drop-down list should automatically get focus when the page loads.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<select autofocus>
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="cars">Choose a car:</label>
<select name="cars" id="cars" autofocus>
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
<option value="opel">Opel</option>
<option value="audi">Audi</option>
</select>

How to add HTML <select> disabled Attribute with label Tag
A disabled drop-down list.
Definition and Usage
The disabled attribute is a boolean attribute.
When present, it specifies that the drop-down list should be disabled.
A disabled drop-down list is unusable and un-clickable.
The disabled attribute can be set to keep a user from using the drop-down list until some other condition has been met (like selecting a checkbox, etc.). Then, a JavaScript can remove the disabled value, and make the drop-down list usable.
Browser Support

Syntax
<select disabled>
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="cars">Choose a car:</label>
<select name="cars" id="cars" disabled>
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
<option value="mercedes">Mercedes</option>
<option value="audi">Audi</option>
</select>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <select> form Attribute with label Tag
A drop-down list located outside a form (but still a part of the form).
Definition and Usage
The form attribute specifies the form the drop-down list belongs to.
The value of this attribute must be equal to the id attribute of a <form> element in the same document.
Browser Support

Syntax
<select form="form_id">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| form_id | Specifies the form element the <select> element belongs to. The value of this attribute must be equal to the id attribute of a <form> element in the same document. |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php" id="carform">
<label for="fname">Firstname:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname">
<input type="submit">
</form>
<label for="cars">Choose a car:</label>
<select name="cars" id="cars" form="carform">
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
<option value="opel">Opel</option>
<option value="audi">Audi</option>
</select>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <select> multiple Attribute with label Tag
A drop-down list that allows multiple selections.
Definition and Usage
The multiple attribute is a boolean attribute.
When present, it specifies that multiple options can be selected at once.
Selecting multiple options vary in different operating systems and browsers:
- For windows: Hold down the control (ctrl) button to select multiple options
- For Mac: Hold down the command button to select multiple options
Because of the different ways of doing this, and because you have to inform the user that multiple selection is available, it is more user-friendly to use checkboxes instead.
Browser Support

Syntax
<select multiple>
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="cars">Choose a car:</label>
<select name="cars" id="cars" multiple>
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
<option value="opel">Opel</option>
<option value="audi">Audi</option>
</select>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <select> name Attribute with label Tag
A drop-down list with a name attribute.
Definition and Usage
The name attribute specifies the name for a drop-down list.
The name attribute is used to reference elements in a JavaScript, or to reference form data after a form is submitted.
Browser Support

Syntax
<select name="text">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| text | The name of the drop-down list |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="cars">Choose a car:</label>
<select name="cars" id="cars">
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
<option value="opel">Opel</option>
<option value="audi">Audi</option>
</select>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <select> required Attribute with label Tag
An HTML form with a required drop-down list.
Definition and Usage
The required attribute is a boolean attribute.
When present, it specifies the user is required to select a value before submitting the form.
Browser Support

Syntax
<select required>
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="cars">Choose a car:</label>
<select name="cars" id="cars" required>
<option value="">None</option>
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
<option value="mercedes">Mercedes</option>
<option value="audi">Audi</option>
</select>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <select> size Attribute with label Tag
A drop-down list with three visible options.
Definition and Usage
The size attribute specifies the number of visible options in a drop-down list.
If the value of the size attribute is greater than 1, but lower than the total number of options in the list, the browser will add a scroll bar to indicate that there are more options to view.
Browser Support

Note: In Chrome and Safari, this attribute may not work as expected for size="2" and size="3".
Syntax
<select size="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | The number of visible options in the drop-down list. Default value is 1. If the multiple attribute is present, the default value is 4 |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="cars">Choose a car:</label>
<select name="cars" id="cars" size="3">
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
<option value="opel">Opel</option>
<option value="audi">Audi</option>
</select>
Output should be:

How to Use <select> with <optgroup> label tags
Follow the Example.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="cars">Choose a car:</label>
<select name="cars" id="cars">
<optgroup label="Swedish Cars">
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
</optgroup>
<optgroup label="German Cars">
<option value="mercedes">Mercedes</option>
<option value="audi">Audi</option>
</optgroup>
</select>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> Attributes with label Tag
A multi-line text input control (text area).
Definition and Usage
The <textarea> tag defines a multi-line text input control.
The <textarea> element is often used in a form, to collect user inputs like comments or reviews.
A text area can hold an unlimited number of characters, and the text renders in a fixed-width font (usually Courier).
The size of a text area is specified by the cols and rows attributes (or with CSS).
The name attribute is needed to reference the form data after the form is submitted (if you omit the name attribute, no data from the text area will be submitted).
The id attribute is needed to associate the text area with a label.
Tip: Always add the <label> tag for best accessibility practices!
Browser Support

Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| autofocus | autofocus | Specifies that a text area should automatically get focus when the page loads |
| cols | number | Specifies the visible width of a text area |
| dirname | textareaname.dir | Specifies that the text direction of the textarea will be submitted |
| disabled | disabled | Specifies that a text area should be disabled |
| form | form_id | Specifies which form the text area belongs to |
| maxlength | number | Specifies the maximum number of characters allowed in the text area |
| name | text | Specifies a name for a text area |
| placeholder | text | Specifies a short hint that describes the expected value of a text area |
| readonly | readonly | Specifies that a text area should be read-only |
| required | required | Specifies that a text area is required/must be filled out |
| rows | number | Specifies the visible number of lines in a text area |
| wrap | hard soft |
Specifies how the text in a text area is to be wrapped when submitted in a form |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="w3review">Review of Horje:</label>
<textarea id="w3review" name="w3review" rows="4" cols="50">
At horje.com you will learn how to make a website. They offer free tutorials in all web development technologies.
</textarea>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> autofocus Attribute with label Tag
A text area with autofocus.
Definition and Usage
The autofocus attribute is a boolean attribute.
When present, it specifies that the text area should automatically get focus when the page loads.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<textarea autofocus>
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="css">Type</label><br>
<textarea autofocus>
At horje.com you will learn how to make a website. We offer free tutorials in all web development technologies.
</textarea>

How to add HTML <textarea> cols Attribute with label Tag
A text area with a specified height and width.
Definition and Usage
The cols attribute specifies the visible width of a text area.
Tip: The size of a text area can also be set by the CSS height and width properties.
Browser Support

Syntax
<textarea cols="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies the width of the text area (in average character width). Default value is 20 |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="css">Type</label><br>
<textarea rows="4" cols="50">
At horje.com you will learn how to make a website. We offer free tutorials in all web development technologies.
</textarea>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> dirname Attribute with label Tag
An HTML form where the field's text direction will be submitted.
Definition and Usage
The dirname attribute enables the submission of the text direction of the text area.
The dirname attribute's value is always the name of the text area, followed by ".dir".
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<textarea name="myname" dirname="myname.dir"></textarea>
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| name.dir | Specifies that the text direction of the textarea will be submitted. |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The textarea dirname attribute</h1>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="css">Type Text:</label><br>
<textarea name="explanation"dirname="explanation.dir"></textarea></br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<p>When the form is being submitted, the text direction of the textarea will also be submitted.</p>
</body>
</html>

How to add HTML <textarea> disabled Attribute with label Tag
A disabled text area.
Definition and Usage
The disabled attribute is a boolean attribute.
When present, it specifies that the text area should be disabled.
A disabled text area is unusable and the text is not selectable (cannot be copied).
The disabled attribute can be set to keep a user from using the text area until some other condition has been met (like selecting a checkbox, etc.). Then, a JavaScript could remove the disabled value, and make the text area usable.
Browser Support

Syntax
<textarea disabled>
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="css">Type Text:</label><br>
<textarea disabled>
At Horje.com you will learn how to make a website. We offer free tutorials in all web development technologies.
</textarea>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> form Attribute with label Tag
A text area located outside a form (but still a part of the form).
Definition and Usage
The form attribute specifies the form the text area belongs to.
The value of this attribute must be equal to the id attribute of a <form> element in the same document.
Browser Support

Syntax
<textarea form="form_id">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| form_id | Specifies the form element the <textarea> element belongs to. The value of this attribute must be the id attribute of a <form> element in the same document. |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="css">Type Text:</label><br>
<textarea rows="4" cols="50" name="comment" form="usrform">
Enter text here...</textarea>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> maxlength Attribute with label Tag
Definition and Usage
The maxlength attribute specifies the maximum length (in characters) of a text area.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<textarea maxlength="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | The maximum number of characters allowed in the text area |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The textarea maxlength attribute</h1>
<label for="text">Type</label><br>
<textarea rows="4" cols="50" maxlength="50">
Enter text here...</textarea>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> name Attribute with label Tag Part 2
A text area with a name attribute:
Definition and Usage
The name attribute specifies a name for a text area.
The name attribute is used to reference elements in a JavaScript, or to reference form data after a form is submitted.
Browser Support

Syntax
<textarea name="text">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| text | Specifies the name of the text area |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="text">Type</label><br>
<textarea rows="4" cols="50" name="comment">
Enter text here...</textarea>
<input type="submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> placeholder Attribute with label Tag
A text area with a placeholder text.
Definition and Usage
The placeholder attribute specifies a short hint that describes the expected value of a text area.
The short hint is displayed in the text area before the user enters a value.
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<textarea placeholder="text">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| text | Specifies a short hint that describes the expected value of the text area |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="text">Who are you?</label><br>
<textarea rows="4" cols="50" placeholder="Describe yourself here..."></textarea>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> readonly Attribute with label Tag
A read-only text area.
Definition and Usage
The readonly attribute is a boolean attribute.
When present, it specifies that a text area should be read-only.
In a read-only text area, the content cannot be changed, but a user can tab to it, highlight it and copy content from it.
The readonly attribute can be set to keep a user from using a text area until some other condition has been met (like selecting a checkbox, etc.). Then, a JavaScript is required to remove the readonly value, and make the text area editable.
Browser Support

Syntax
<textarea readonly>
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="text">Type</label><br>
<textarea rows="4" cols="50" readonly>
At horje.com you will learn how to make a website. We offer free tutorials in all web development technologies.
</textarea>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> required Attribute with label Tag
A form with a required text area.
Definition and Usage
The required attribute is a boolean attribute.
When present, it specifies that a text area is required/must be filled out (in order to submit the form).
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the attribute.

Syntax
<textarea required>
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="text">Type</label><br>
<textarea rows="4" cols="50" name="comment" required>
</textarea>
<input type="submit">
</form>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> rows Attribute with label Tag
A text area with a specified height and width.
Definition and Usage
The rows attribute specifies the visible height of a text area, in lines.
Note: The size of a textarea can also be specified by the CSS height and width properties.
Browser Support

Syntax
<textarea rows="number">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Specifies the height of the text area (in lines). Default value is 2 |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<label for="text">Type</label><br>
<textarea rows="4" cols="50">
At horje.com you will learn how to make a website. We offer free tutorials in all web development technologies.
</textarea>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> wrap Attribute with label Tag
The text in a text area with wrap="hard" will contain newlines (if any) when submitted in a form.
Definition and Usage
The wrap attribute specifies how the text in a text area is to be wrapped when submitted in a form.
Browser Support

Syntax
<textarea wrap="soft|hard">
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| soft | The text in the textarea is not wrapped when submitted in a form. This is default |
| hard | The text in the textarea is wrapped (contains newlines) when submitted in a form. When "hard" is used, the cols attribute must be specified |
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The textarea wrap attribute</h1>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="text">Type</label><br>
<textarea rows="2" cols="20" name="usrtxt" wrap="hard">
At Horje you will find free Web-building tutorials.
</textarea>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> wrap soft Attribute with label Tag
The text in a text area with wrap="soft" will contain newlines (if any) when submitted in a form.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The textarea wrap attribute</h1>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="html">HTML</label><br>
<textarea rows="2" cols="20" name="usrtxt" wrap="soft">
At Horje you will find free Web-building tutorials.
</textarea>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

How to add HTML <textarea> wrap hard Attribute with label Tag
The text in a text area with wrap="hard" will contain newlines (if any) when submitted in a form:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The textarea wrap attribute</h1>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="html">HTML</label><br>
<textarea rows="2" cols="20" name="usrtxt" wrap="hard">
At Horje you will find free Web-building tutorials.
</textarea>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

Category: | Web Tutorial |
Sub Category: | HTML Tag |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
