Tips (Total 25)
# Tips-1) What is HTML Input Attributes
This chapter describes the different attributes for the HTML <input> element.
The <input> HTML element is used to create interactive controls for web-based forms in order to accept data from the user; a wide variety of types of input data and control widgets are available, depending on the device and user agent. The <input> element is one of the most powerful and complex in all of HTML due to the sheer number of combinations of input types and attributes.
# Tips-2) How to create HTML The value Attribute
The input value attribute specifies an initial value for an input field:
How is to look HTML The value Attribute
Input fields with initial (default) values:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John"><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Example of HTML The value Attribute
The value attribute specifies an initial value for an input field:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input value attribute</h1>
<p>The value attribute specifies an initial value for an input field:</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John"><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-3) How to create HTML readonly Attribute
The input readonly attribute specifies that an input field is read-only.
A read-only input field cannot be modified (however, a user can tab to it, highlight it, and copy the text from it).The value of a read-only input field will be sent when submitting the form!
How is to look HTML readonly Attribute
A read-only input field:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John" readonly><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe">
</form>
Full Code Example of HTML readonly Attribute
The input readonly attribute The readonly attribute specifies that an input field should be read-only (cannot be changed):
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input readonly attribute</h1>
<p>The readonly attribute specifies that an input field should be read-only (cannot be changed):</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John" readonly><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-4) How to create HTML disabled Attribute in input
The input disabled attribute specifies that an input field should be disabled.
A disabled input field is unusable and un-clickable.
The value of a disabled input field will not be sent when submitting the form!
How is to look HTML disabled Attribute in input
A disabled input field:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John" disabled><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Code Example of HTML disabled Attribute in input
The input disabled attribute The disabled attribute specifies that an input field should be disabled (unusable and un-clickable):
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input disabled attribute</h1>
<p>The disabled attribute specifies that an input field should be disabled (unusable and un-clickable):</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John" disabled><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-5) How to edit HTML size Attribute in input
The input size attribute specifies the visible width, in characters, of an input field.
The default value for size is 20.
Note: The size attribute works with the following input types: text, search, tel, url, email, and password.
How is to look HTML size Attribute in input
Set a width for an input field:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" size="50"><br>
<label for="pin">PIN:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="pin" name="pin" size="4">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Code Example of HTML size Attribute in input
The input size attribute The size attribute specifies the width (in characters) of an input field:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input size attribute</h1>
<p>The size attribute specifies the width (in characters) of an input field:</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" size="50"><br>
<label for="pin">PIN:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="pin" name="pin" size="4"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-6) How to create HTML maxlength Attribute in input
The input maxlength attribute specifies the maximum number of characters allowed in an input field.
Note: When a maxlength is set, the input field will not accept more than the specified number of characters. However, this attribute does not provide any feedback. So, if you want to alert the user, you must write JavaScript code.
How is to look HTML maxlength Attribute in input
Set a maximum length for an input field:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" size="50"><br>
<label for="pin">PIN:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="pin" name="pin" maxlength="4" size="4">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Code Example of HTML maxlength Attribute in input
The maxlength attribute specifies the maximum number of characters allowed in an input field:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input maxlength attribute</h1>
<p>The maxlength attribute specifies the maximum number of characters allowed in an input field:</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" size="50"><br>
<label for="pin">PIN:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="pin" name="pin" maxlength="4" size="4"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-7) How to create HTML min and max Attributes
The input min and max attributes specify the minimum and maximum values for an input field.
The min and max attributes work with the following input types: number, range, date, datetime-local, month, time and week.
Tip: Use the max and min attributes together to create a range of legal values.
How is to look HTML min and max Attributes
Set a max date, a min date, and a range of legal values:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="datemax">Enter a date before 1980-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemax" name="datemax" max="1979-12-31"><br><br>
<label for="datemin">Enter a date after 2000-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemin" name="datemin" min="2000-01-02"><br><br>
<label for="quantity">Quantity (between 1 and 5):</label>
<input type="number" id="quantity" name="quantity" min="1" max="5">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Code Example of HTML min and max Attributes
Set a max date, a min date, and a range of legal values:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input min and max attributes</h1>
<p>The min and max attributes specify the minimum and maximum values for an input element.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="datemax">Enter a date before 1980-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemax" name="datemax" max="1979-12-31"><br><br>
<label for="datemin">Enter a date after 2000-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemin" name="datemin" min="2000-01-02"><br><br>
<label for="quantity">Quantity (between 1 and 5):</label>
<input type="number" id="quantity" name="quantity" min="1" max="5"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-8) How to create HTML multiple Attribute
The input multiple attribute specifies that the user is allowed to enter more than one value in an input field.
The multiple attribute works with the following input types: email, and file.
How is to look HTML multiple Attribute
A file upload field that accepts multiple values:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="files">Select files:</label>
<input type="file" id="files" name="files" multiple>
</form>
Output should be:

Full Code Example of HTML multiple Attribute
The multiple attribute specifies that the user is allowed to enter more than one value in an input field.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input multiple attributes</h1>
<p>The multiple attribute specifies that the user is allowed to enter more than one value in an input field.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="files">Select files:</label>
<input type="file" id="files" name="files" multiple><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<p>To select multiple files, hold down the CTRL or SHIFT key while selecting.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-9) How to build HTML pattern Attribute in input
The input pattern attribute specifies a regular expression that the input field's value is checked against, when the form is submitted.
The pattern attribute works with the following input types: text, date, search, url, tel, email, and password.
Tip: Use the global title attribute to describe the pattern to help the user.
Tip: Learn more about regular expressions in our JavaScript tutorial.
How to look HTML pattern Attribute in input
An input field that can contain only three letters (no numbers or special characters):
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="country_code">Country code:</label>
<input type="text" id="country_code" name="country_code"
pattern="[A-Za-z]{3}" title="Three letter country code">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Example of HTML pattern Attribute in input
The pattern attribute specifies a regular expression that the input element's value is checked against.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
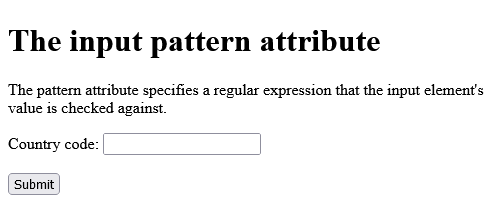
<h1>The input pattern attribute</h1>
<p>The pattern attribute specifies a regular expression that the input element's value is checked against.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="country_code">Country code:</label>
<input type="text" id="country_code" name="country_code" pattern="[A-Za-z]{3}" title="Three letter country code"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:
# Tips-10) How to set HTML placeholder Attribute
The input placeholder attribute specifies a short hint that describes the expected value of an input field (a sample value or a short description of the expected format).
The short hint is displayed in the input field before the user enters a value.
The placeholder attribute works with the following input types: text, search, url, tel, email, and password.
How is to look HTML placeholder Attribute
An input field with a placeholder text:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="phone">Enter a phone number:</label>
<input type="tel" id="phone" name="phone"
placeholder="123-45-678"
pattern="[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{3}">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Code Example of HTML placeholder Attribute
The input placeholder attribute The placeholder attribute specifies a short hint that describes the expected value of an input field.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input placeholder attribute</h1>
<p>The placeholder attribute specifies a short hint that describes the expected value of an input field.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="phone">Enter a phone number:</label>
<input type="tel" id="phone" name="phone" placeholder="123-45-678" pattern="[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{3}"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-11) How to create HTML required Attribute in input
The input required attribute specifies that an input field must be filled out before submitting the form.
The required attribute works with the following input types: text, search, url, tel, email, password, date pickers, number, checkbox, radio, and file.
How is to look HTML required Attribute
A required input field:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" required>
</form>
Output should be:

Full Code Example of HTML required Attribute
The input required attribute The required attribute specifies that an input field must be filled out before submitting the form.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
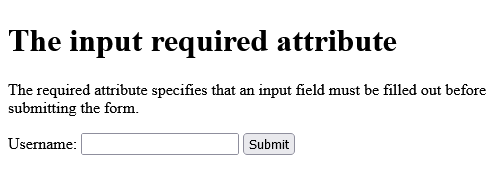
<h1>The input required attribute</h1>
<p>The required attribute specifies that an input field must be filled out before submitting the form.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" required>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:
# Tips-12) How to create HTML step Attribute in input
The input step attribute specifies the legal number intervals for an input field.
Example: if step="3", legal numbers could be -3, 0, 3, 6, etc.
Tip: This attribute can be used together with the max and min attributes to create a range of legal values.
The step attribute works with the following input types: number, range, date, datetime-local, month, time and week.
How is to look HTML step Attribute in input
An input field with a specified legal number intervals:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="points">Points:</label>
<input type="number" id="points" name="points" step="3">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Code Example of HTML step Attribute in input
The input step attribute The step attribute specifies the legal number intervals for an input element.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input step attribute</h1>
<p>The step attribute specifies the legal number intervals for an input element.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="points">Points:</label>
<input type="number" id="points" name="points" step="3">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

Note: Input restrictions are not foolproof, and JavaScript provides many ways to add illegal input. To safely restrict input, it must also be checked by the receiver (the server)!
# Tips-13) How to set HTML autofocus Attribute in input
The input autofocus attribute specifies that an input field should automatically get focus when the page loads.
Hoow is to look HTML autofocus Attribute
Let the "First name" input field automatically get focus when the page loads:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" autofocus><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Code Example of HTML autofocus Attribute
The input autofocus attribute The autofocus attribute specifies that the input field should automatically get focus when the page loads.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input autofocus attribute</h1>
<p>The autofocus attribute specifies that the input field should automatically get focus when the page loads.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" autofocus><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-14) How to add height and width Attributes in HTML Input
The input height and width attributes specify the height and width of an <input type="image"> element.
Tip: Always specify both the height and width attributes for images. If height and width are set, the space required for the image is reserved when the page is loaded. Without these attributes, the browser does not know the size of the image, and cannot reserve the appropriate space to it. The effect will be that the page layout will change during loading (while the images load).
Example of adding height and width Attributes in HTML Input
Define an image as the submit button, with height and width attributes:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<input type="image" src="img_submit.gif" alt="Submit" width="48" height="48">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Completed Code example of adding height and width Attributes in HTML Input
The height and width attributes specify the height and width of an input type="image" element.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input height and width attributes</h1>
<p>The height and width attributes specify the height and width of an input type="image" element.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<input type="image" src="img_submit.gif" alt="Submit" width="48" height="48">
</form>
<p><b>Note:</b> The input type="image" sends the X and Y coordinates of the click that activated the image button.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-15) How to create HTML list Attribute in input
The input list attribute refers to a <datalist> element that contains pre-defined options for an <input> element.
Example of HTML list Attribute in input
An <input> element with pre-defined values in a <datalist>:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form>
<input list="browsers">
<datalist id="browsers">
<option value="Edge">
<option value="Firefox">
<option value="Chrome">
<option value="Opera">
<option value="Safari">
</datalist>
</form>
Output should be:

Full Completed Code Example of HTML list Attribute in input
The input list attribute The list attribute refers to a datalist element that contains pre-defined options for an input element.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input list attribute</h1>
<p>The list attribute refers to a datalist element that contains pre-defined options for an input element.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<input list="browsers" name="browser">
<datalist id="browsers">
<option value="Edge">
<option value="Firefox">
<option value="Chrome">
<option value="Opera">
<option value="Safari">
</datalist>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-16) How to add HTML autocomplete Attribute in Input
The input autocomplete attribute specifies whether a form or an input field should have autocomplete on or off.
Autocomplete allows the browser to predict the value. When a user starts to type in a field, the browser should display options to fill in the field, based on earlier typed values.
The autocomplete attribute works with <form> and the following <input> types: text, search, url, tel, email, password, datepickers, range, and color.
Example of ADDING HTML autocomplete Attribute in Input
An HTML form with autocomplete on, and off for one input field:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php" autocomplete="on">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" autocomplete="off"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Completed code Example of ADDING HTML autocomplete Attribute in Input
The autocomplete attribute The autocomplete attribute specifies whether or not an input field should have autocomplete enabled. Fill in and submit the form, then reload the page to see how autocomplete works. Notice that autocomplete is "on" for the form, but "off" for the e-mail field!
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The autocomplete attribute</h1>
<p>The autocomplete attribute specifies whether or not an input field should have autocomplete enabled.</p>
<p>Fill in and submit the form, then reload the page to see how autocomplete works.</p>
<p>Notice that autocomplete is "on" for the form, but "off" for the e-mail field!</p>
<form action="/action_page.php" autocomplete="on">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" autocomplete="off"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-17) What is HTML Input form Attributes
This chapter describes the different form* attributes for the HTML element.
Example
An input field located outside of the HTML form (but still a part of the form):
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input form attribute</h1>
<p>The form attribute specifies the form an input element belongs to.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php" id="form1">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<p>The "Last name" field below is outside the form element, but still part of the form.</p>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" form="form1">
</body>
</html>
Output should be:
# Tips-18) How to create HTML form Attribute in Input
The input form attribute specifies the form the <input> element belongs to.
The value of this attribute must be equal to the id attribute of the <form> element it belongs to.
Example of creating HTML form Attribute in Input
An input field located outside of the HTML form (but still a part of the form):
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php" id="form1">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" form="form1">
Output should be:

Full Completed Code of creating HTML form Attribute in Input
The form attribute specifies the form an input element belongs to. The "Last name" field below is outside the form element, but still part of the form.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
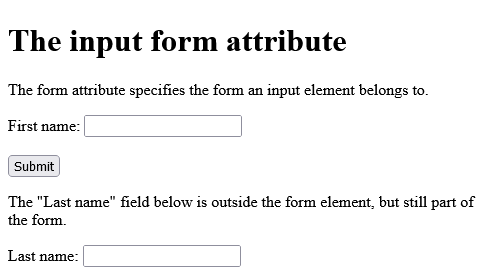
<h1>The input form attribute</h1>
<p>The form attribute specifies the form an input element belongs to.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php" id="form1">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<p>The "Last name" field below is outside the form element, but still part of the form.</p>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" form="form1">
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-19) How to set HTML form action Attribute in Input
The input formaction attribute specifies the URL of the file that will process the input when the form is submitted.
Note: This attribute overrides the action attribute of the <form> element.
The formaction attribute works with the following input types: submit and image.
Example of HTML form action Attribute in Input
An HTML form with two submit buttons, with different actions:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formaction="/action_page2.php" value="Submit as Admin">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Example of HTML form action Attribute in Input
The input formaction attribute The formaction attribute specifies the URL of a file that will process the input when the form is submitted.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input formaction attribute</h1>
<p>The formaction attribute specifies the URL of a file that will process the input when the form is submitted.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formaction="/action_page2.php" value="Submit as Admin">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-20) How to set HTML formenctype Attribute in input
The input formenctype attribute specifies how the form-data should be encoded when submitted (only for forms with method="post").
Note: This attribute overrides the enctype attribute of the
element.
The formenctype attribute works with the following input types: submit and image.
Example of HTML formenctype Attribute in input
A form with two submit buttons. The first sends the form-data with default encoding, the second sends the form-data encoded as "multipart/form-data":
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page_binary.asp" method="post">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formenctype="multipart/form-data"
value="Submit as Multipart/form-data">
</form>
Output should be:

Full of HTML formenctype Attribute in input
The input formenctype attribute The formenctype attribute specifies how the form data should be encoded when submitted.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input formenctype attribute</h1>
<p>The formenctype attribute specifies how the form data should be encoded when submitted.</p>
<form action="/action_page_binary.asp" method="post">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formenctype="multipart/form-data" value="Submit as Multipart/form-data">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-21) How to set HTML form method Attribute in Input
The input formmethod attribute defines the HTTP method for sending form-data to the action URL.
Note: This attribute overrides the method attribute of the <form> element.
The formmethod attribute works with the following input types: submit and image.
The form-data can be sent as URL variables (method="get") or as an HTTP post transaction (method="post").
Notes on the "get" method:
- This method appends the form-data to the URL in name/value pairs
- This method is useful for form submissions where a user want to bookmark the result
- There is a limit to how much data you can place in a URL (varies between browsers), therefore, you cannot be sure that all of the form-data will be correctly transferred
- Never use the "get" method to pass sensitive information! (password or other sensitive information will be visible in the browser's address bar)
Notes on the "post" method:
- This method sends the form-data as an HTTP post transaction
- Form submissions with the "post" method cannot be bookmarked
- The "post" method is more robust and secure than "get", and "post" does not have size limitations
Example of HTML form method Attribute in Input
A form with two submit buttons. The first sends the form-data with method="get". The second sends the form-data with method="post":
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php" method="get">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit using GET">
<input type="submit" formmethod="post" value="Submit using POST">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Example of HTML form method Attribute in Input
The input formmethod Attribute The formmethod attribute defines the HTTP method for sending form-data to the action URL.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input formmethod Attribute</h1>
<p>The formmethod attribute defines the HTTP method for sending form-data to the action URL.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php" method="get" target="_blank">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit using GET">
<input type="submit" formmethod="post" value="Submit using POST">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-22) How to set HTML form target Attribute in Input
The input formtarget attribute specifies a name or a keyword that indicates where to display the response that is received after submitting the form.
Note: This attribute overrides the target attribute of the <form> element.
The formtarget attribute works with the following input types: submit and image.
Example of HTML form target Attribute in Input
A form with two submit buttons, with different target windows:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formtarget="_blank" value="Submit to a new window/tab">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Example of HTML form target Attribute in Input
The input formtarget attribute The formtarget attribute specifies a name or a keyword that indicates where to display the response that is received after submitting the form.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input formtarget attribute</h1>
<p>The formtarget attribute specifies a name or a keyword that indicates where to display the response that is received after submitting the form.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formtarget="_blank" value="Submit to a new window/tab">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-23) How to set HTML formnovalidate Attribute in Input
The input formnovalidate attribute specifies that an <input> element should not be validated when submitted.
Note: This attribute overrides the novalidate attribute of the <form> element.
The formnovalidate attribute works with the following input types: submit.
Example of HTML formnovalidate Attribute in Input
A form with two submit buttons (with and without validation):
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="email">Enter your email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formnovalidate="formnovalidate"
value="Submit without validation">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Example of HTML formnovalidate Attribute in Input
The input formnovalidate attribute
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The input formnovalidate attribute</h1>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="email">Enter your email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formnovalidate="formnovalidate" value="Submit without validation">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-24) How to set HTML novalidate Attribute in Input
The novalidate attribute is an attribute.
When present, novalidate specifies that all of the form-data should not be validated when submitted.
Example of HTML novalidate Attribute in Input
Specify that no form-data should be validated on submit:
index.html
Example:
HTML
<form action="/action_page.php" novalidate>
<label for="email">Enter your email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Output should be:

Full Example of HTML novalidate Attribute in Input
The form novalidate attribute The novalidate attribute specifies that the form data should not be validated when submitted.
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The form novalidate attribute</h1>
<p>The novalidate attribute specifies that the form data should not be validated when submitted.</p>
<form action="/action_page.php" novalidate>
<label for="email">Enter your email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:

# Tips-25) How to create HTML Video - Methods, Properties, and Events using Javascript
This tutorial will add some options.
- Video Play/Pause button.
- Video Play Big
- Video Play Small
- Video Play Normal
The HTML DOM defines methods, properties, and events for the element.
This allows you to load, play, and pause videos, as well as setting duration and volume.
There are also DOM events that can notify you when a video begins to play, is paused, etc.
Example of HTML Video - Methods, Properties, and Events using Javascript
Example: Using JavaScript
index.html
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div style="text-align:center">
<button onclick="playPause()">Play/Pause</button>
<button onclick="makeBig()">Big</button>
<button onclick="makeSmall()">Small</button>
<button onclick="makeNormal()">Normal</button>
<br><br>
<video id="video1" width="420">
<source src="https://www.w3schools.com/html/mov_bbb.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="https://www.w3schools.com/html/mov_bbb.mp4" type="video/ogg">
Your browser does not support HTML video.
</video>
</div>
<script>
var myVideo = document.getElementById("video1");
function playPause() {
if (myVideo.paused)
myVideo.play();
else
myVideo.pause();
}
function makeBig() {
myVideo.width = 560;
}
function makeSmall() {
myVideo.width = 320;
}
function makeNormal() {
myVideo.width = 420;
}
</script>
<p>Video courtesy of <a href="https://www.bigbuckbunny.org/" target="_blank">Big Buck Bunny</a>.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output should be:
